Heal Your Gut, Heal Your Life: The Gundry Health Approach to Leaky Gut and Autoimmune Disease
The gut is the foundation of overall health, influencing everything from immune function to mental well-being. When compromised, it can trigger a cascade of chronic illnesses, including autoimmune diseases. At Gundry Health, we understand that leaky gut syndrome (LGS) is a hidden epidemic, affecting millions of people and leading to inflammation, food sensitivities, and systemic disorders.
What Is Leaky Gut Syndrome?
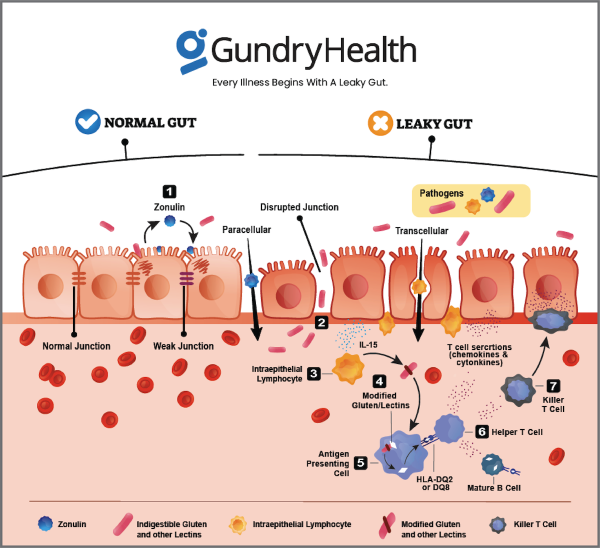
Leaky gut syndrome occurs when the lining of the small intestine becomes damaged, creating tiny gaps that allow toxins, bacteria, and undigested food particles to enter the bloodstream. This breach in the intestinal barrier activates the immune system, leading to widespread inflammation and increasing the risk of autoimmune diseases such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
Dr. Steven Gundry, a pioneer in gut health and autoimmune disease treatment, emphasizes that most chronic illnesses originate in the gut. Research shows that over 80% of the immune system resides in the gut, making its health crucial for preventing and reversing disease.
The Castle Analogy: Understanding Gut Defenses
Think of your gut as a medieval fortress:
- Fortress Walls: Your intestinal lining acts as a barrier to protect against harmful invaders.
- Guards: Beneficial bacteria serve as sentries, ensuring only nutrients pass through.
- Moat: A mucus barrier shields the walls from potential harm.
- Messengers: The gut-brain axis communicates with the brain (the command center) to monitor gut health.
When poor diet choices, stress, toxins, and medications weaken these defenses, the walls deteriorate (leaky gut), the guards abandon their posts (microbial imbalance), and invaders (harmful substances) infiltrate, leading to chronic health conditions.
The Gut-Brain Connection
Nearly 90% of serotonin—a neurotransmitter responsible for mood regulation—is produced in the gut. A compromised gut can disrupt this balance, leading to anxiety, depression, and cognitive issues. Gundry Health prioritizes gut healing as a core strategy for restoring mental and physical wellness.
Leaky Gut’s Role in Autoimmune Diseases
Leaky gut is a primary trigger for autoimmune diseases. When foreign particles pass through the gut barrier into the bloodstream, the immune system misidentifies them as threats and begins attacking the body’s own tissues. Comprehensive testing and personalized treatment are essential to address gut dysfunction and halt autoimmune reactions.
Common Conditions Linked to Leaky Gut:
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Often caused by bacterial overgrowth and food sensitivities.
- Lupus: Disruptions in gut flora and chronic inflammation contribute to symptoms.
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): Gluten and dairy sensitivities exacerbate symptoms.
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: Leaky gut contributes to thyroid autoimmunity.
- Arthritis: Microbial infections can trigger joint inflammation.
- Skin Disorders: Eczema, psoriasis, and rosacea often stem from gut imbalances.
Gundry Health’s Gut Healing Strategy
1. Dietary Overhaul
- Remove inflammatory foods (gluten, dairy, refined sugars).
- Follow a whole-food, nutrient-rich diet full of fiber, polyphenols, and omega-3s.
- Integrate fermented foods and prebiotics to cultivate a thriving gut microbiome.
2. Hydration & Detoxification
- Consume half your body weight (lbs) in ounces of water daily to stay hydrated.
- Support detox pathways with herbal treatments and intermittent fasting.
3. Restoring Microbial Balance
- Use probiotics and prebiotics to reestablish beneficial gut flora.
- Follow a microbiome-supporting diet with resistant starches and diverse plant foods.
4. Addressing Hormonal & Immune System Imbalances
- Optimize thyroid, adrenal, and sex hormone levels to support digestive function.
- Reduce inflammation with targeted supplementation, including vitamin D, zinc, and magnesium.
5. Lifestyle & Stress Management
- Chronic stress weakens gut integrity—mindfulness, meditation, and acupuncture are effective healing tools.
- Consistent exercise and movement enhance gut motility and immune resilience.
Success Stories
Angela’s Transformation: Overcoming IBS and Chronic Gut Pain
Angela, a 33-year-old registered nurse, suffered from severe bloating, IBS, and stomach pain for a year. Traditional treatments failed her, as no doctors addressed her diet. Gundry Health’s comprehensive gut analysis identified a casein (dairy) sensitivity and H. pylori infection. After adopting a tailored gut-healing protocol, she experienced complete symptom relief within eight weeks. Today, Angela enjoys optimal digestion and a pain-free life.
The Future of Autoimmune Disease Treatment
Traditional medicine often focuses on symptom management rather than root causes. At Gundry Health, we take a holistic, evidence-based approach to healing. By tackling leaky gut, we empower patients to reverse autoimmune diseases naturally and restore their well-being.
🚀 Ready to Restore Your Gut and Reclaim Your Health?
Join Gundry Health’s advanced telemedicine program and take charge of your wellness journey. A healthier you starts today!
📞 Schedule Your Consultation Now!
🔗 Visit GundryHealth.com for More Information.
#GundryHealth #LeakyGut #AutoimmuneHealing #GutRestoration #DrStevenGundry #Telemedicine #FunctionalMedicine #HealthyLiving
Essential Questions & Answers About Leaky Gut & Autoimmune Health
What Is Leaky Gut Syndrome and How Does It Develop?
Leaky gut syndrome, also known as increased intestinal permeability, is a condition where the protective lining of the small intestine becomes compromised. This damage creates small openings in the intestinal barrier, allowing unwanted substances such as toxins, undigested food particles, and harmful bacteria to pass into the bloodstream.
The intestinal lining functions as a selective filter, permitting essential nutrients to be absorbed while preventing harmful substances from entering circulation. However, when the tight junctions between gut cells weaken, they fail to maintain this barrier, leading to increased permeability. Several factors contribute to this breakdown, including a diet high in processed foods, chronic stress, excessive use of medications (such as antibiotics and NSAIDs), infections, and an imbalance in gut bacteria.
Once foreign particles enter the bloodstream, the immune system identifies them as threats, triggering an inflammatory response. This ongoing immune reaction can lead to chronic inflammation, contributing to a range of health issues and increasing the risk of autoimmune diseases. Over time, leaky gut can perpetuate a cycle of worsening intestinal permeability and systemic inflammation.
How Does Inflammation Relate to Leaky Gut Syndrome?
Inflammation plays a dual role in leaky gut syndrome, acting as both a cause and a consequence of increased intestinal permeability. When the gut lining becomes inflamed, it weakens the tight junctions between cells, allowing harmful substances to seep into the bloodstream. In turn, these foreign substances stimulate an immune response, further exacerbating inflammation throughout the body.
The body’s inflammatory response involves numerous signaling molecules, such as cytokines, that alert the immune system to potential threats. While acute inflammation is a protective mechanism designed to aid healing, chronic inflammation stemming from leaky gut can become detrimental. Persistent inflammation disrupts normal cellular functions and has been linked to a wide range of health concerns, including digestive disorders, autoimmune conditions, and metabolic diseases.
Effectively managing inflammation through dietary modifications, stress reduction, and targeted supplementation is essential in addressing leaky gut and restoring gut health.
What Role Do Gut Bacteria Play in Overall Health?
The human gut is home to trillions of microorganisms, collectively known as the gut microbiota. These beneficial bacteria play a crucial role in digestion, immune function, and overall health. A balanced gut microbiome aids in breaking down food, synthesizing essential vitamins, and preventing harmful pathogens from taking hold in the digestive tract.
When the composition of gut bacteria becomes imbalanced—a condition known as dysbiosis—it can lead to increased intestinal permeability and systemic inflammation. Factors such as poor dietary choices, chronic stress, antibiotic use, and environmental toxins can disrupt the balance of beneficial and harmful bacteria.
Maintaining a healthy microbiome is essential for optimal digestion, efficient nutrient absorption, and immune system regulation. A diet rich in fiber, probiotics, and prebiotics can help promote a thriving gut environment, reducing the risk of leaky gut and its associated health concerns.
How Does the Digestive System Normally Function?
The digestive system is a complex network of organs working together to process food, extract nutrients, and eliminate waste. Digestion begins in the mouth, where enzymes in saliva start breaking down carbohydrates. Food then travels through the esophagus into the stomach, where gastric juices and muscular contractions further break it down.
From the stomach, partially digested food moves into the small intestine, where most nutrient absorption occurs. The small intestine contains millions of tiny finger-like projections called villi, which increase surface area for maximum absorption. Essential nutrients pass through the intestinal wall into the bloodstream to nourish the body.
The remaining undigested material enters the large intestine, where beneficial bacteria help ferment fiber, absorb water, and produce certain vitamins. Eventually, waste products are expelled from the body through bowel movements. A properly functioning digestive system is vital for overall health, ensuring that nutrients are efficiently absorbed while toxins and waste are effectively eliminated.
What Is the Connection Between Leaky Gut and Autoimmune Conditions?
Leaky gut syndrome is increasingly recognized as a key factor in the development of autoimmune diseases. When the intestinal barrier becomes compromised, foreign proteins, bacteria, and toxins can enter the bloodstream. This triggers an immune response that may mistakenly target the body’s own tissues, leading to autoimmune disorders.
Research suggests that many autoimmune conditions, including type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis, are linked to intestinal permeability. When the immune system remains in a heightened state of alert due to continuous exposure to foreign particles, it can lose its ability to differentiate between harmful invaders and the body’s own cells.
Addressing leaky gut through diet, lifestyle changes, and gut-supportive therapies can help reduce immune overactivation and support overall health.
How Do Hormones Affect Gut Health?
Hormones play a critical role in regulating digestion, gut motility, and intestinal integrity. Several key hormones influence gut health, including:
- Thyroid hormones, which regulate metabolism and ensure proper digestive function.
- Cortisol, a stress hormone that can weaken the gut barrier when chronically elevated.
- Estrogen and progesterone, which impact gut motility and microbiome composition.
When hormone levels become imbalanced, it can contribute to digestive issues, inflammation, and increased gut permeability. Chronic stress, poor sleep, and dietary factors all influence hormone balance and, in turn, affect gut health. Supporting hormonal balance through stress management, adequate sleep, and proper nutrition is crucial for maintaining a healthy digestive system.
What Are the Most Common Symptoms of Leaky Gut Syndrome?
Leaky gut syndrome manifests in a variety of symptoms, which can affect different systems in the body. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Digestive issues such as bloating, gas, diarrhea, and constipation
- Food sensitivities and intolerances, particularly to gluten and dairy
- Nutrient deficiencies despite a seemingly adequate diet
- Chronic fatigue and low energy levels
- Brain fog, difficulty concentrating, and mood imbalances
- Joint pain and muscle aches
- Skin problems such as acne, eczema, and psoriasis
- Increased susceptibility to infections and autoimmune conditions
Because these symptoms can overlap with other health issues, addressing gut health is a foundational step in restoring overall wellness.
How Does Stress Impact Gut Health?
The gut and brain are intimately connected through the gut-brain axis, meaning emotional and psychological stress directly affect digestive function. When the body perceives stress, it releases hormones that can alter gut motility, increase intestinal permeability, and disrupt the balance of gut bacteria.
Chronic stress not only exacerbates leaky gut but also contributes to digestive issues, anxiety, and depression. Many of the body’s neurotransmitters, including serotonin, are produced in the gut, highlighting the strong link between emotional well-being and gut health.
Managing stress through mindfulness practices, exercise, proper nutrition, and gut-supportive supplements is essential for maintaining a healthy gut barrier and overall well-being.
Why Is Gut Flora Balance Essential for Health?
A balanced gut microbiome is essential for optimal health, as it influences digestion, immune function, and even mental well-being. Beneficial bacteria help break down food, produce vital nutrients, and protect against harmful pathogens.
When gut flora becomes imbalanced, it can contribute to inflammation, increased intestinal permeability, and various chronic health conditions. Factors such as a poor diet, antibiotics, stress, and environmental toxins can disrupt microbial diversity.
Supporting gut flora balance through a diet rich in fermented foods, fiber, and prebiotics can help maintain a healthy gut environment, promoting overall well-being and reducing the risk of digestive and autoimmune disorders.
How Does Hydration Impact Gut Health?
Staying properly hydrated is essential for optimal gut health. Water plays a vital role in breaking down food, ensuring efficient digestion, and facilitating the transport of essential nutrients throughout the body. It also helps maintain the protective mucus lining of the intestines, which acts as a barrier against harmful pathogens and toxins. The amount of water needed for proper hydration varies by individual, but a simple calculation involves dividing one’s weight in pounds by two to determine the recommended daily water intake in ounces.
Dehydration can have a profound impact on digestive health, leading to constipation, increased inflammation, and reduced nutrient absorption. Furthermore, it is important to note that beverages like coffee, soda, and other caffeinated drinks do not contribute to daily hydration needs and can even have a dehydrating effect. Timing of water intake is also critical; drinking too much water during meals may dilute stomach acid, impairing digestion and the breakdown of food. To support gut health, it is best to consume water consistently throughout the day, prioritizing hydration before and after meals rather than during.
How Does Leaky Gut Contribute to Arthritis?
Leaky gut syndrome has been closely linked to arthritis, as compromised intestinal walls allow undigested food particles, bacteria, and toxins to enter the bloodstream. This triggers an immune system response, leading to systemic inflammation that can affect the joints and contribute to arthritis-related symptoms. This connection has been recognized for over a century, with various infectious agents, including bacteria, viruses, parasites, and yeast, implicated in different forms of arthritis. Among these, mycoplasma bacteria are believed to be a primary contributor to certain arthritic conditions.
Conventional arthritis treatments, such as NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) and corticosteroids, often fail to address the root cause of inflammation and may even exacerbate intestinal permeability. A more effective approach involves addressing gut health holistically through dietary modifications, targeted supplementation, and treatment of underlying infections. Patients who adopt a gut-healing approach often experience significant relief from arthritis symptoms without the need for long-term medication use.
What is the Link Between Gut Health and Diabetes?
The relationship between gut health and diabetes is significant, as both dietary and inflammatory factors contribute to metabolic disorders. In type 2 diabetes, excessive consumption of refined foods and sugars disrupts gut microbiota, leading to chronic inflammation and insulin resistance. This condition is not purely genetic but is largely influenced by modern dietary habits and a sedentary lifestyle.
Type 1 diabetes, an autoimmune condition, is closely associated with increased intestinal permeability. When the gut lining is compromised, foreign substances can enter the bloodstream, triggering an immune response against pancreatic cells responsible for insulin production. Research from the Diabetes Research Institute in Milan has demonstrated that individuals with type 1 diabetes exhibit distinct gut inflammation and microbiome imbalances compared to both healthy individuals and those with other autoimmune disorders. Addressing gut health through dietary intervention and probiotic supplementation may help mitigate the severity of diabetic conditions and improve overall metabolic function.
How Does Leaky Gut Syndrome Affect Multiple Sclerosis (MS)?
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a neurodegenerative autoimmune condition that involves the breakdown of myelin, the protective coating around nerve fibers in the central nervous system. Emerging research suggests a strong link between gut inflammation and the autoimmune response that targets myelin. Many MS patients exhibit elevated levels of gluten antibodies, indicating a sensitivity to certain foods that may exacerbate inflammation and trigger immune attacks on nerve tissue.
Eliminating inflammatory foods such as gluten and dairy has been shown to improve symptoms in MS patients. In addition to dietary modifications, a comprehensive approach that includes hormone balancing with bioidentical hormones and correction of nutrient deficiencies can lead to significant improvements. Some patients following a gut-healing regimen have even achieved complete remission, demonstrating the profound impact of gut health on neurological conditions.
What is the Connection Between Gut Health and Lupus?
Lupus is an autoimmune condition that affects over 1.5 million Americans, characterized by the immune system attacking the body’s own tissues. Recent studies have identified disrupted gut flora as a common finding in lupus patients, suggesting that gut health plays a key role in disease progression. Imbalances in gut bacteria contribute to systemic inflammation and immune dysfunction, further exacerbating lupus symptoms.
Healing the gut through dietary interventions, including the elimination of inflammatory foods such as dairy and gluten, has been shown to be highly effective in managing lupus symptoms. Many patients experience symptom relief when they follow a gut-healing protocol that includes targeted supplementation and natural therapies. Unlike conventional treatments that rely heavily on immunosuppressants, an integrative approach that addresses gut health can help regulate immune function without compromising overall health.
How Does Leaky Gut Syndrome Contribute to Skin Conditions?
The health of the gut is directly reflected in the skin, making gut integrity a crucial factor in managing skin conditions. Research shows that more than half of acne sufferers have underlying gut flora imbalances, and this pattern extends to other chronic skin conditions such as rosacea, psoriasis, and eczema. Since both the skin and gut function as barrier organs, any disruption in the gut’s protective lining can trigger systemic inflammation, which often manifests as skin problems.
Leaky gut syndrome allows toxins and undigested food particles to enter the bloodstream, leading to inflammatory responses that contribute to blemishes, rashes, and other skin disorders. Patients with persistent skin issues often experience dramatic improvements when they adopt a gut-healing protocol, which includes removing inflammatory foods, replenishing beneficial gut bacteria, and repairing the gut lining with targeted nutrients.
What is the Connection Between Gut Health and Asthma/Allergies?
Asthma and allergies are immune system disorders that often originate from gut inflammation and increased intestinal permeability. When the gut barrier becomes compromised, it allows foreign substances to enter the bloodstream, triggering allergic reactions and inflammatory responses in various parts of the body, including the respiratory system.
One of the most effective approaches for managing these conditions involves gut healing strategies that reduce inflammation and restore gut integrity. The Nambudripad’s Allergy Elimination Technique (NAET) has shown significant success in treating allergies and asthma by addressing the body’s energetic response to allergens while simultaneously improving gut health. Many patients experience long-term relief from allergy and asthma symptoms after implementing dietary changes and gut-healing protocols.
How is Hashimoto’s Disease Linked to Gut Health?
Hashimoto’s disease, an autoimmune thyroid disorder, is closely tied to gut health due to the immune system’s response to increased intestinal permeability. When the gut lining is compromised, proteins and bacteria leak into the bloodstream, triggering an immune attack that can damage the thyroid gland.
Healing the gut through an anti-inflammatory diet, removal of trigger foods (such as gluten and dairy), and supplementation with gut-supportive nutrients has been shown to significantly improve Hashimoto’s symptoms. Many patients experience better thyroid function and reduced autoimmune activity when they follow a comprehensive gut-healing approach alongside proper thyroid hormone support.
What is the Relationship Between IBS and Leaky Gut?
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is often a symptom of underlying gut permeability issues. It is frequently triggered by food allergies, bacterial overgrowth, and microbial imbalances, all of which contribute to inflammation and digestive distress.
Treatment for IBS should focus on identifying and eliminating problematic foods while restoring gut balance with targeted supplementation. Most individuals see noticeable improvements within six to eight weeks of dietary changes, but symptoms may return if trigger foods are reintroduced. A long-term strategy that addresses both gut permeability and microbial balance is key to managing IBS effectively.
How Can You Test for Leaky Gut Syndrome?
Diagnosing leaky gut syndrome requires a multi-faceted approach, as no single test can provide a complete picture of gut permeability and dysfunction. One of the most effective diagnostic tools is a comprehensive stool analysis. This test evaluates bacterial balance, digestive function, and inflammatory markers, offering insight into the presence of harmful bacteria, yeast overgrowth, and parasitic infections. It helps determine whether the gut microbiome is imbalanced and if inflammation is present, both of which can contribute to leaky gut symptoms.
Blood testing is another valuable diagnostic tool. It identifies food sensitivities, nutritional deficiencies, and inflammatory markers that may indicate an impaired gut barrier. Other specialized tests include hair analysis for assessing mineral imbalances, the Heidelberg test for measuring stomach acid levels, and specific laboratory assessments designed to measure intestinal permeability. A combination of these diagnostic approaches provides a well-rounded understanding of gut health and guides targeted treatment strategies.
How Does Hair Analysis Help Identify Nutritional Deficiencies?
Hair mineral analysis is a non-invasive diagnostic tool that offers a long-term view of an individual’s nutritional status. Unlike blood or urine tests, which reflect short-term fluctuations, hair analysis captures a biochemical record of mineral deposits over several months. By assessing these mineral patterns, the test can detect chronic nutritional imbalances and toxin accumulation that may not be evident in traditional testing methods.
This diagnostic method is particularly useful for identifying deficiencies in essential minerals such as magnesium, zinc, and selenium—nutrients that play a crucial role in gut function and overall health. Additionally, hair analysis can reveal exposure to heavy metals like mercury and lead, which can contribute to digestive dysfunction and systemic inflammation. By pinpointing these imbalances, healthcare providers can recommend targeted nutritional interventions to restore optimal health.
Why Is Stool Testing Essential for Gut Health Diagnosis?
Stool testing provides an in-depth assessment of digestive health by analyzing enzyme production, nutrient absorption, and the presence of pathogenic organisms. It identifies bacterial imbalances, parasitic infections, and yeast overgrowth, all of which can contribute to gastrointestinal distress and systemic inflammation.
Furthermore, stool analysis measures markers of gut inflammation and immune function, helping to determine whether the intestinal barrier is compromised. A poorly functioning gut can result in malabsorption of essential nutrients, leading to deficiencies that impact overall health. By addressing the findings of a stool test, healthcare practitioners can develop personalized treatment plans to restore microbial balance, improve digestion, and support gut healing.
Which Blood Tests Are Most Relevant for Gut Health?
Several blood tests play a crucial role in evaluating gut health and identifying underlying issues that may be contributing to digestive symptoms. A complete blood count (CBC) can detect signs of infection, anemia, or inflammation. Comprehensive metabolic panels assess liver and kidney function, electrolyte balance, and blood sugar levels—factors that can be influenced by gut health.
Additionally, antibody tests can detect food sensitivities, autoimmune markers, and signs of chronic inflammation, all of which can indicate gut dysfunction. Nutrient status tests for vitamins and minerals, such as B vitamins, vitamin D, and magnesium, help assess whether malabsorption is occurring. Hormonal testing, including thyroid function, cortisol levels, and sex hormones, can further reveal how gut health influences systemic regulation and overall well-being.
How Do Doctors Determine Food Sensitivities?
Food sensitivities are often a hidden cause of chronic inflammation and gut dysfunction. Blood tests that measure IgG and IgA antibody responses to specific foods provide valuable information about potential sensitivities. However, elimination diets remain the gold standard for identifying problematic foods. This method involves removing common inflammatory foods—such as gluten, dairy, and processed foods—for a period of at least six weeks, then systematically reintroducing them while monitoring symptoms.
Another approach to food sensitivity testing includes NAET (Nambudripad’s Allergy Elimination Techniques), which utilizes muscle testing and energy assessments to identify sensitivities. Combining laboratory testing with an elimination diet provides a comprehensive understanding of an individual’s unique triggers, allowing for personalized dietary recommendations that support gut healing and overall wellness.
How Does Gut Health Influence Mental Health?
The gut and brain are intricately connected through the gut-brain axis, a bidirectional communication system that involves the nervous system, immune system, and microbial balance. The enteric nervous system, often referred to as the “second brain,” contains millions of nerve cells that interact with the brain via the vagus nerve and neurotransmitter production.
Approximately 90% of serotonin, the neurotransmitter responsible for mood regulation, is produced in the gut. When gut health is compromised—whether due to dysbiosis, leaky gut, or chronic inflammation—it can negatively impact mood, cognition, and emotional well-being. Research has linked gut imbalances to conditions such as anxiety, depression, and brain fog. Addressing gut health through dietary changes, probiotics, and stress management can significantly improve mental health outcomes.
What Is the Link Between Gut Health and Alzheimer’s Disease?
Recent research suggests a strong correlation between gut health and cognitive function, particularly in relation to Alzheimer’s disease. Dysbiosis, or an imbalance in gut bacteria, has been shown to contribute to neuroinflammation and amyloid plaque formation in the brain—key factors in the progression of Alzheimer’s.
Certain food additives, emulsifiers, and processed ingredients have been linked to chronic gut inflammation, which can exacerbate cognitive decline. The gut-brain axis plays a crucial role in neuroprotection, and maintaining a healthy gut microbiome may reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases. Dietary modifications, anti-inflammatory interventions, and probiotic supplementation can help support brain health by improving gut function and reducing systemic inflammation.
How Does Gut Health Impact ADHD?
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) has been closely linked to gut health, with studies showing that up to 64% of ADHD cases are associated with food hypersensitivities. Common dietary triggers include dairy, gluten, artificial food colorings, and preservatives, all of which can contribute to gut inflammation and neurotransmitter imbalances.
Additionally, children and adults with ADHD often exhibit nutritional deficiencies in omega-3 fatty acids, magnesium, zinc, and B vitamins—nutrients essential for brain function and impulse control. Addressing these deficiencies through targeted supplementation and a gut-friendly diet can lead to significant improvements in focus, behavior, and overall well-being.
How Is Depression Connected to Gut Health?
Depression is increasingly recognized as a disorder with strong ties to gut health. The gut microbiome plays a vital role in producing and regulating neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and GABA, all of which influence mood and emotional stability. When the gut barrier is compromised, inflammatory molecules can enter the bloodstream, triggering neuroinflammation and contributing to depressive symptoms.
Studies have shown that individuals with depression often have altered gut microbiomes and higher levels of systemic inflammation. Restoring gut health through dietary modifications, prebiotics, probiotics, and stress management strategies can significantly enhance mental well-being and alleviate depressive symptoms.
How Does the Gut Communicate with the Brain?
The gut communicates with the brain through several key pathways, including the vagus nerve, immune signaling, and neurotransmitter production. The enteric nervous system (ENS) contains over 100 million nerve cells that regulate digestion while sending signals to the brain about nutrient status, microbial balance, and potential threats.
Additionally, gut bacteria produce neuroactive compounds that influence mood, cognition, and immune function. The health of the gut directly impacts brain health, making gut care an essential component of overall well-being. Strategies such as maintaining a balanced diet, reducing stress, and supporting a diverse gut microbiome can optimize the gut-brain connection and enhance mental clarity, focus, and emotional health.
What is the best diet for repairing a leaky gut?
The most effective diet for repairing a leaky gut focuses on whole, nutrient-dense, unprocessed foods while avoiding refined sugars, processed grains, and inflammatory ingredients. A Paleo-inspired eating plan is ideal, emphasizing lean, high-quality proteins, fresh, organic vegetables and fruits, and healthy fats that provide the essential nutrients necessary for gut repair.
It is crucial to eliminate common trigger foods that contribute to gut inflammation and intestinal permeability, including gluten, dairy, refined vegetable oils, and artificial additives. Instead, prioritize anti-inflammatory foods rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that support the body’s natural healing mechanisms.
Additionally, incorporating fermented foods like sauerkraut, kimchi, and probiotic-rich yogurt or kefir can help replenish beneficial gut bacteria, improving digestion and immune function. High-fiber vegetables such as leafy greens, asparagus, and artichokes provide prebiotic fiber that nourishes these beneficial microbes, further promoting gut health. Hydration also plays a key role, with an optimal water intake of at least half your body weight in ounces per day to support digestion, detoxification, and overall healing.
How do refined foods negatively impact gut health?
Refined and processed foods are stripped of their natural nutrients, including essential vitamins, minerals, fiber, and enzymes, making them nutritionally deficient and difficult to digest. While these foods have a longer shelf life, they offer little benefit to the body and instead contribute to inflammation and digestive disturbances.
Many refined products contain harmful additives, preservatives, artificial flavorings, and emulsifiers that can irritate the gut lining and disrupt the balance of healthy gut bacteria. Consuming these processed foods forces the body to use its own nutrient reserves to process them, leading to nutrient depletion over time.
Regular consumption of refined carbohydrates and processed snacks can cause blood sugar fluctuations, increased gut permeability, and an overgrowth of harmful bacteria, setting the stage for chronic inflammation and digestive disorders. To heal the gut, it is essential to replace these foods with whole, natural ingredients that provide the body with the necessary nutrients to repair and maintain intestinal integrity.
How do carbohydrates impact gut health?
Carbohydrates serve as a primary energy source for both the body and gut microbiota, but their effects on gut health vary depending on the type and source. Complex carbohydrates from whole foods, such as vegetables, fruits, and legumes, contain essential fiber and prebiotics that support digestion and nourish beneficial gut bacteria.
These complex carbohydrates break down slowly in the digestive tract, promoting stable blood sugar levels and reducing inflammation. In contrast, simple carbohydrates, particularly those found in refined and processed foods, digest quickly, causing rapid blood sugar spikes that can lead to gut dysbiosis, inflammation, and increased intestinal permeability.
The glycemic index (GI) of carbohydrates helps determine their impact on blood sugar levels. Lower-GI foods, such as sweet potatoes, quinoa, and non-starchy vegetables, are preferable for gut health, as they provide steady energy while promoting microbial diversity. A diet focused on unrefined, fiber-rich carbohydrates supports optimal digestion and long-term gut integrity.
Why is protein essential for gut healing?
Protein is a fundamental building block for tissue repair, cell regeneration, and immune function, making it essential for healing a leaky gut. High-quality proteins supply amino acids, such as glutamine, which directly support intestinal cell renewal and gut lining repair.
The source of protein matters significantly. Organic, grass-fed meats, pasture-raised poultry, wild-caught fish, and collagen-rich bone broth provide the highest-quality nutrients without the added hormones and antibiotics commonly found in conventionally raised meats. These sources also contain beneficial omega-3 fatty acids that help reduce inflammation in the digestive tract.
For those following a plant-based diet, incorporating a variety of complementary protein sources, such as lentils, quinoa, hemp seeds, and fermented soy products, ensures all essential amino acids are obtained. The goal is to consume high-quality proteins that aid in gut lining restoration and support digestive enzyme production for optimal gut function.
Which fats are beneficial for gut health, and which should be avoided?
Healthy fats play a crucial role in maintaining gut integrity by reducing inflammation, supporting cell membranes, and aiding in nutrient absorption. The best fats for gut health include omega-3 fatty acids found in wild-caught fish, grass-fed meats, pasture-raised eggs, and plant-based sources such as flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. Extra virgin olive oil, coconut oil, and avocado oil provide additional anti-inflammatory benefits and help maintain a healthy gut lining.
Conversely, unhealthy fats, such as trans fats, hydrogenated oils, and refined vegetable oils (e.g., soybean, corn, and canola oils), are highly inflammatory and can damage gut cells, contributing to increased intestinal permeability. These harmful fats are commonly found in processed snacks, fast foods, and commercially baked goods, making it essential to avoid them when following a gut-healing diet.
Why is gluten problematic for many individuals?
Gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, can trigger an inflammatory response in the gut, leading to increased intestinal permeability, commonly referred to as “leaky gut.” This occurs due to gluten’s ability to stimulate the release of zonulin, a protein that regulates tight junctions in the intestinal lining. Excessive zonulin release can weaken these junctions, allowing toxins and undigested food particles to enter the bloodstream and trigger immune responses.
This reaction is not limited to those with celiac disease; many individuals experience gluten sensitivity that manifests in digestive discomfort, skin conditions, neurological symptoms, and autoimmune flare-ups. Because modern wheat contains higher gluten levels than ancient grains, it has become increasingly problematic for gut health. To test for gluten sensitivity, it is best to eliminate it completely for several weeks and monitor symptoms before reintroducing it.
How does dairy impact gut health?
Dairy products, particularly those containing casein protein and lactose, can be difficult to digest and may contribute to inflammation and gut permeability in sensitive individuals. Conventional dairy often contains added hormones and antibiotics, further disrupting gut balance and potentially leading to food intolerances and autoimmune responses.
However, fermented dairy products such as kefir, yogurt, and aged cheeses contain beneficial probiotics that can support gut health when well-tolerated. Choosing high-quality, organic, grass-fed dairy or opting for non-dairy alternatives like almond or coconut-based products can help minimize gut irritation while still providing essential nutrients.
How do artificial sweeteners affect gut health?
Artificial sweeteners, including aspartame, sucralose, and saccharin, have been shown to negatively impact gut microbiota by altering bacterial composition, reducing microbial diversity, and promoting inflammation. These synthetic compounds can interfere with blood sugar regulation and metabolism, potentially leading to glucose intolerance and increased intestinal permeability.
Avoiding artificial sweeteners and opting for natural alternatives can help protect gut health and prevent metabolic disturbances.
What are the best natural sweeteners for gut health?
Natural sweeteners like raw honey, maple syrup, and stevia offer a gut-friendly alternative when used in moderation. Raw honey contains antimicrobial properties and prebiotics that support beneficial bacteria, while pure maple syrup provides trace minerals that aid digestion. Choosing these natural options over artificial sweeteners can help support gut balance.
Which foods actively promote gut healing?
Gut-healing foods include bone broth, fermented vegetables, leafy greens, and fiber-rich prebiotic foods. Anti-inflammatory spices like turmeric, ginger, and garlic provide additional support by reducing inflammation and enhancing microbial balance. Incorporating these foods into a well-balanced diet promotes optimal digestion and long-term gut health.
How does NAET therapy help in managing allergies?
Nambudripad’s Allergy Elimination Technique (NAET) is a holistic approach designed to identify and treat allergies by addressing disruptions in the body’s energy flow. Through a method called muscle testing (applied kinesiology), NAET practitioners determine which substances are causing energetic imbalances. Once these allergens are identified, acupressure techniques are used to help the body reset its response to them.
During treatment, the problematic substance is introduced into the patient’s energy field while specific acupressure points along the meridian system are stimulated. This process helps retrain the body’s immune system, allowing it to adapt to these substances without triggering an allergic reaction. NAET is particularly effective for individuals with food allergies, environmental sensitivities, and multiple chemical sensitivities, providing long-term relief by addressing the root cause of allergic responses rather than merely suppressing symptoms.
NAET integrates principles from acupuncture, chiropractic care, and traditional Chinese medicine to help restore balance within the body. By strengthening the body’s natural defense system and eliminating energetic blockages, this approach promotes overall wellness and resilience against allergens.
Why are probiotics essential for gut health?
Probiotics are live beneficial bacteria that play a vital role in maintaining a balanced gut microbiome. They support digestive function, aid in nutrient absorption, and help regulate the immune system. A well-balanced gut flora contributes to overall health by preventing harmful bacteria from taking over and promoting a diverse ecosystem within the digestive tract.
Probiotics are particularly helpful in breaking down food, producing essential vitamins (such as B12 and K2), and strengthening the gut barrier. By fostering a healthy microbial environment, they reduce inflammation and enhance the body’s ability to fight infections. Certain strains, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, have been shown to support immune function, improve digestion, and reduce symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
Regular consumption of probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi, or taking a high-quality probiotic supplement, can help replenish beneficial bacteria, particularly after antibiotic use or periods of digestive distress. Maintaining a balanced gut microbiome is essential for long-term gut health, as it influences everything from mood and energy levels to immune function and metabolic health.
How do prebiotics contribute to gut healing?
Prebiotics are a type of dietary fiber that serves as food for beneficial gut bacteria. Unlike probiotics, which introduce new bacteria into the gut, prebiotics help nourish and support the growth of existing beneficial microbes. By fostering the right conditions for good bacteria to thrive, prebiotics play a crucial role in maintaining gut health and preventing harmful bacterial overgrowth.
Common sources of prebiotics include fiber-rich vegetables (such as garlic, onions, leeks, and asparagus), whole grains, bananas, and fermented foods. These foods contain compounds like inulin and fructooligosaccharides, which selectively feed beneficial bacteria in the colon.
Prebiotics contribute to gut healing by enhancing nutrient absorption, improving gut barrier function, and reducing inflammation. When paired with probiotics—a combination known as synbiotics—they create an optimal environment for microbial balance and digestive wellness. For individuals with gut health concerns, incorporating prebiotic foods or supplements can be a powerful tool for long-term digestive support.
What are the most important supplements for gut health?
A well-rounded approach to gut health often includes key supplements that support digestion, reduce inflammation, and promote gut lining repair. Essential nutrients that contribute to optimal gut function include:
- Vitamin D: Plays a crucial role in immune regulation and maintaining gut barrier integrity. Deficiencies are linked to increased gut permeability and digestive disorders.
- Magnesium: Supports muscle relaxation, aiding in bowel regularity and reducing symptoms of constipation or digestive discomfort.
- Zinc: Helps heal the gut lining and supports immune function, making it particularly important for those with leaky gut syndrome.
- Vitamin B12: Essential for energy production and nerve function, often deficient in individuals with gut malabsorption issues.
- L-Glutamine: An amino acid that serves as fuel for intestinal cells, helping repair the gut lining and reduce inflammation.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Reduce systemic inflammation, which can contribute to conditions like IBS and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
- Digestive Enzymes: Aid in the breakdown and absorption of food, alleviating bloating, gas, and malabsorption issues.
- Herbal Supplements: Oregano oil and mastic gum help control bacterial overgrowth and support a balanced microbiome.
The right combination of supplements varies based on individual needs, gut health status, and dietary habits. Consulting with a healthcare provider to determine the most beneficial regimen can help optimize gut health and overall well-being.
How does acupuncture aid in gut healing?
Acupuncture is an ancient healing practice that stimulates specific points along the body’s meridian system to restore balance and promote healing. When applied to digestive health, acupuncture helps regulate the nervous system, improve gut motility, and reduce inflammation—factors that are crucial for individuals struggling with gut disorders.
By targeting acupuncture points associated with digestion, practitioners can help alleviate symptoms of bloating, indigestion, acid reflux, and constipation. Acupuncture has also been shown to balance the autonomic nervous system, reducing the body’s stress response, which can significantly impact gut function. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with stress-induced gut issues such as IBS.
Additionally, acupuncture enhances circulation to the digestive organs, supporting efficient nutrient absorption and waste elimination. As part of an integrative gut health strategy, acupuncture can complement dietary changes and other therapies to improve overall digestive well-being.
How can someone transition to a gut-healthy diet?
Adopting a gut-friendly diet should be done gradually to allow the digestive system to adjust. The key steps include:
- Eliminate inflammatory foods: Remove processed foods, refined sugars, artificial additives, and common allergens like gluten and dairy.
- Introduce whole, nutrient-dense foods: Focus on fiber-rich vegetables, lean proteins, healthy fats, and fermented foods to promote beneficial bacteria.
- Hydrate properly: Drink adequate amounts of water to support digestion and detoxification.
- Adopt mindful eating habits: Chew food thoroughly, eat in a relaxed state, and avoid overeating to reduce digestive strain.
- Gradual implementation: Rather than making drastic changes, incorporate gut-friendly foods progressively to prevent digestive discomfort.
Following a structured approach ensures a smoother transition and sustainable long-term results in gut health improvement.
What lifestyle changes support gut healing?
In addition to dietary modifications, lifestyle factors play a crucial role in gut health. Key changes include:
- Managing stress: Chronic stress disrupts gut function and increases inflammation. Practices such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can promote relaxation.
- Prioritizing sleep: Poor sleep quality negatively impacts gut microbiome balance. Aim for 7-9 hours of restorative sleep each night.
- Staying active: Regular physical activity supports gut motility and overall digestive function.
- Hydration: Drinking sufficient water throughout the day aids in digestion and detoxification.
- Establishing consistent eating patterns: Eating meals at regular intervals and avoiding late-night snacking support optimal digestion and metabolism.
By combining these lifestyle habits with dietary improvements, individuals can foster long-term gut health and overall wellness.