Dr. Steven Gundry explains the cause of eczema and suggests a new way to diagnose and treat this autoimmune disease.
Discover the symptoms and types of eczema and learn the simple steps you can take to feel better if you’re suffering from Eczema.
What is Eczema?
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes the skin to become inflamed and itchy. People with eczema often have a personal or family history of other autoimmune diseases, such as asthma or hay fever. Eczema is a common chronic autoimmune disease that affects people of all ages.
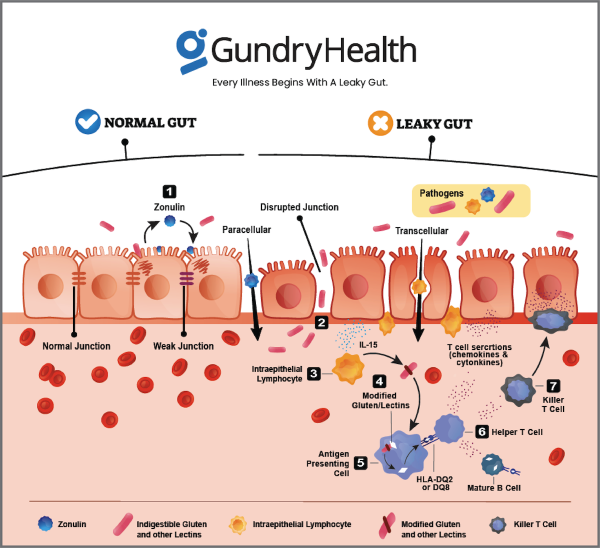
The gut is lined with a layer of cells known as the epithelium, which acts as a barrier to prevent bacteria and other potentially harmful substances from entering the body. In a condition known as leaky gut, the epithelial barrier becomes damaged, allowing bacteria and other substances to pass through and enter the bloodstream. This can trigger an immune response, which may lead to the development of eczema.
Additionally, the gut microbiome, which is the community of microorganisms that live in the gut, is thought to play a role in the development of eczema. Research has shown that individuals with eczema have a different gut microbiome composition compared to individuals without eczema. It is thought that imbalances in the gut microbiome may contribute to the development of eczema by altering the immune system and the barrier function of the gut.
What are the symptoms of Eczema?
The symptoms of eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual. However, some common symptoms of eczema include:
- Red, itchy patches of skin
- Dry, scaly skin
- Cracked or thickened skin
- Raw, sensitive skin
- Dark-colored patches of skin
- Swelling or bumps on the skin
In addition to these symptoms, individuals with eczema may also experience:
- Blisters that may ooze or crust over
- Pain or burning sensations on the skin
- Scratching that can cause the skin to become infected
- Difficulty sleeping due to severe itching
- Changes in skin color or texture
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider. They can help to diagnose your condition and recommend the appropriate treatment options.
What are the different types of Eczema?
There are different types of eczema. The most common type is atopic dermatitis, which is often referred to simply as eczema. This type of eczema is typically chronic and tends to occur in individuals who have a family history of allergies, such as hay fever or asthma
Other types of eczema include:
- Contact dermatitis: This type of eczema is caused by contact with an irritant or allergen, such as a chemical or a certain type of clothing.
- Dyshidrotic eczema: This type of eczema causes small, itchy blisters to form on the hands and feet.
- Neurodermatitis: This type of eczema is characterized by thick, scaly patches of skin that are caused by chronic itching and scratching.
- Nummular eczema: This type of eczema is characterized by coin-shaped patches of scaly, itchy skin.
- Stasis dermatitis: This type of eczema is caused by poor circulation in the legs, which can cause swelling, itching, and irritation.
The symptoms and treatment options for each type of eczema can vary, so it is important to speak with a healthcare provider to determine the type of eczema you have and the best course of treatment.
What causes Eczema?
Contributing factor to the development of eczema is a condition known as leaky gut syndrome. This is a condition in which the small intestine’s lining becomes damaged, allowing bacteria and toxins to leak into the bloodstream. This can trigger an immune response, leading to inflammation and other symptoms.
It is difficult to estimate exactly how many people around the world are suffering from eczema, as the prevalence of the disease can vary depending on a number of factors, including age, gender, and geographic location. However, it is estimated that eczema affects approximately 10-20% of children and 1-3% of adults worldwide.
Eczema is more common in developed countries, and It is thought that the increased prevalence of eczema in developed countries may be due to environmental factors, such as exposure to chemicals and pollutants, as well as lifestyle factors, such as increased stress and changes in diet. While the exact prevalence of the disease is difficult to determine, it is estimated to affect millions of people worldwide. Continued research is needed to better understand the causes of eczema and to develop more effective treatments.
How to treat Eczema?
Historical treatment for eczema typically involves a combination of moisturizers, anti-inflammatory medications, and avoidance of triggers that can worsen symptoms. In severe cases, immunosuppressive drugs may be necessary to control the immune system and reduce inflammation.
One expert in the treatment of eczema and other autoimmune diseases is Dr. Steven Gundry. Dr. Gundry is a renowned cardiologist and author who has dedicated his career to helping people with autoimmune conditions. He has developed a unique approach to treating autoimmune diseases, which focuses on identifying and eliminating the underlying causes of inflammation.
In his book “The Plant Paradox,” Dr. Gundry discusses the role that diet can play in the development and management of autoimmune diseases, including eczema. He recommends a diet low in lectins, which are proteins found in many plants that can trigger an immune response. By avoiding foods high in lectins and incorporating other anti-inflammatory foods into the diet, Dr. Gundry believes that it is possible to manage and even reverse autoimmune conditions.
Overall, eczema is a chronic autoimmune disease that can be difficult to manage, but with the right treatment and lifestyle changes, it is possible to control symptoms and improve quality of life. By working with a healthcare provider and incorporating the recommendations of experts like Dr. Gundry, individuals with eczema can take an active role in their own health and well-being.
Dr. Gundry’s Yes / No Food List and Lectin-free Diet
The lectin-free diet is a dietary approach that focuses on avoiding lectins, proteins found in many plants. Lectins have been linked to an increased risk of autoimmune disease and other health problems, so avoiding them may help reduce symptoms of existing conditions or prevent new ones from developing. By avoiding lectins, the lectin-free diet can help reduce inflammation and promote long-term health.
The lectin-free diet typically involves eliminating foods that are high in lectins such as grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. It also requires limiting intake of processed foods that may contain lectins as preservatives or binders. Additionally, the lectin-free diet often includes eating a variety of fresh in season fruits and vegetables as well as replacing some grain-based carbohydrates with starchy vegetables like sweet potatoes or beets .
When following a lectin-free diet, it is important to incorporate plenty of healthy fats such as olive oil, avocado oil, and coconut oil. Healthy fats can provide the energy needed for daily activities and can help reduce inflammation in those with autoimmune diseases like eczema. Additionally, adding fermented foods to the diet can help improve gut health and reduce inflammation. Probiotic rich foods such as goat cheese , sauerkraut, kimchi and kombucha are all excellent sources of beneficial bacteria that can support digestive health.
Download your free copy of Dr. Gundry’s Yes No Food List here!
In addition to dietary changes it is important to also manage stress levels by engaging in relaxation techniques like yoga or mindfulness meditation on a regular basis. Reducing stress can help calm an overactive immune system which can lead to a reduction in symptoms associated with autoimmune diseases such as eczema.
Overall, a lectin-free diet may help reduce symptoms associated with existing autoimmune conditions as well as improve overall health by reducing inflammation throughout the body. When following this dietary pattern it is important to focus on eating plenty of fresh in season fruits and vegetables while limiting processed foods and incorporating healthy fats into meals. Additionally stress management techniques should be employed regularly in order to keep the immune system balanced and functioning properly
Get your own personalized eczema care and recommendations from Dr Gundry-approved care coordinators
If you’re looking for more guidance than these simple recommendations for eczema, Dr. Gundry’s unique health program is now available to you (without needing an appointment at one of Dr. Gundry’s two, waitlist-only West Coast clinics).
Thanks to the pioneering work of Dr. Gundry and his team at Gundry Health, care coordinators trained in Dr. Gundry’s unique holistic methods are now available to help you craft your own personalized eczema program.